一、利用关联对象给分类添加完整属性
1、分类能添加属性,但不能添加成员变量
2、虽然能添加属性,但添加的是不完整的属性
3、利用关联对象给分类添加完整的属性
4、关联对象的本质
二、获取一个类所有的成员变量。实现一键归档解裆
三、使用Method Swizzling
1、防止button的暴力点击
2、刷新TableView、CollectionView时,自动判断是否该显示暂无数据。
一、利用关联对象给分类添加完整属性
1、分类里能添加属性,但不能添加成员变量
举例来验证下:
假设有一个INEPerson类,并且为它创建了一个分类INEEat。
- 当我们在分类里添加属性时,编译器仅仅报警告说“
name属性需要name方法和setName:方法的实现”,并建议我们“用@dynamic告诉编译器运行时才添加,或者直接在分类里添加这两个方法的实现”,编译能通过就证明:分类里能添加属性。


- 而当我们在分类里添加成员变量时,编译器直接报错说“成员变量不应该放在分类里”,编译报错就证明:分类里不能添加成员变量。
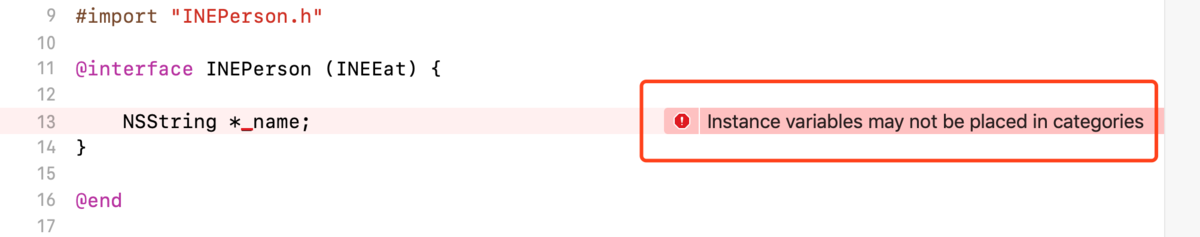
那为什么分类里能添加属性,但不能添加成员变量呢?首先我们知道类的成员变量列表是只读的(类的本质、class_ro_t、ivars那儿还记得吧),所以它在编译后就不能被修改了。其次分类的内部有相应的成员变量来存储该分类为类扩展的方法、属性和协议,但没有特定的成员变量用来存储分类为类扩展的成员变量(分类的本质那儿还记得吧),因此分类能为类扩展属性,但不能为类扩展成员变量。
2、虽然能添加属性,但添加的是不完整的属性
我们都知道,给类添加一个属性,系统其实做了三件事:
- 生成对应的成员变量
- 生成对应
setter、getter方法的声明
- 生成对应
setter、getter方法的实现
我们称这为完整的属性
举例来验证下:
接着第1小节的例子,我们仅仅在INEEat分类里为INEPerson类添加了一个name属性,现在打印一下INEPerson类的实例方法列表、属性列表和成员变量列表。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
| -----------ViewController.m-----------
#import <objc/runtime.h>
#import "INEPerson.h"
- (NSArray *)methodsOfClass:(Class)cls {
NSMutableArray *methods = [@[] mutableCopy];
unsigned int count;
Method *methodList = class_copyMethodList(cls, &count);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
Method method = methodList[I];
NSString *methodName = NSStringFromSelector(method_getName(method));
[methods addObject:methodName];
}
free(methodList);
return methods;
}
- (NSArray *)propsOfClass:(Class)cls {
NSMutableArray *props = [@[] mutableCopy];
unsigned int count;
objc_property_t *propList = class_copyPropertyList(cls, &count);
for (NSInteger i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
objc_property_t property = propList[I];
NSString *propName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:property_getName(property)];
[props addObject:propName];
}
free(propList);
return props;
}
- (NSArray *)ivarsOfClass:(Class)cls {
NSMutableArray *ivars = [@[] mutableCopy];
unsigned int count;
Ivar *ivarList = class_copyIvarList(cls, &count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i ++) {
Ivar ivar = ivarList[I];
NSString *ivarName = [NSString stringWithUTF8String:ivar_getName(ivar)];
[ivars addObject:ivarName];
}
free(ivarList);
return ivars;
}
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSLog(@"实例方法列表:%@", [self methodsOfClass:[INEPerson class]]);
NSLog(@"属性列表:%@", [self propsOfClass:[INEPerson class]]);
NSLog(@"成员变量列表:%@", [self ivarsOfClass:[INEPerson class]]);
}
|
控制台打印如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| 实例方法列表:(
)
属性列表:(
name
)
成员变量列表:(
)
|
可见给分类添加一个属性,确确实实没有生成对应的成员变量,也没有生成对应setter、getter方法的实现(方法只有被实现了,才会被放入类的methods成员变量中)。
此时我们去INEEat分类里,尝试自己实现一下name属性的setter、getter方法,发现方法名敲一半它们会自动弹出来,这就证明name属性的setter、getter方法已经被声明了。
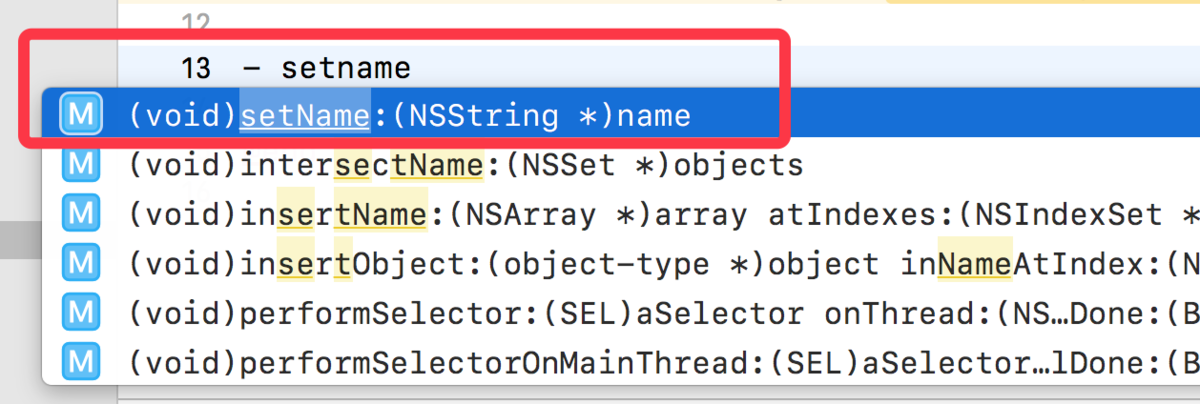
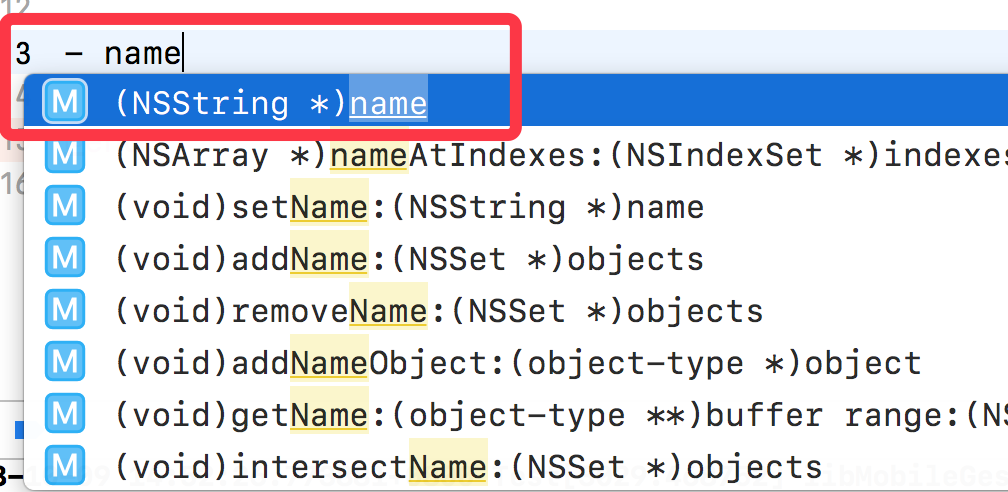
那为什么分类里能添加属性,但仅仅是生成了对应setter、getter方法的声明,而不生成它们的实现呢?这主要还是因为分类内部结构里不能存储成员变量,而导致没有生成属性对应的成员变量,进而导致没法生成setter、getter方法的实现,我们知道setter、getter方法的内部实现不就是给成员变量赋值、取值嘛。
3、利用关联对象给分类添加完整的属性
在开发中,我们肯定会遇到往分类里添加属性的需求,但既然系统不会为我们自动生成对应的成员变量和setter、getter方法的实现,那我们就自己搞成一个完整的属性吧。
自己搞的话,添加一对儿setter、getter方法倒是很简单,难的地方在于它俩的内部实现应该怎么写,也就是说数据要存储在哪里、又从哪里读取,再进一步就是说我们得想办法找一个类似于成员变量那么个东西来存储数据、并从它里面读取数据,要不然setter、getter方法里面没法写啊!当然我们可以自己写一个全局的字典来模拟成员变量那样存取数据,不过要做很多额外的考虑(例如数据是否和对象一对一、数据何时应该销毁、多线程条件下数据写入是否安全等),所以就直接用Runtime给我们提供的关联对象来代替成员变量存储数据吧!关联对象其实就是一个对象,和成员变量的功能差不多,用来帮助我们存储数据和读取数据。
有了代替成员变量的关联对象,我们就可以顺利地自己实现setter、getter方法了,用到的是Runtime的API。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| -----------INEPerson+INEEat.m-----------
#import "INEPerson+INEEat.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@implementation INEPerson (INEEat)
- (void)setName:(NSString *)name {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"name", name, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)name {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"name");
}
@end
|
移除关联对象:
1
2
3
4
5
|
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"name", nil, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object);
|
数据存储策略:
| objc_AssociationPolicy |
对应修饰符 |
| OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN |
assign |
| OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC |
strong、nonatomic |
| OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC |
copy、nonatomic |
| OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN |
strong、atomic |
| OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY |
copy、atomic |
4、关联对象的本质
通过查看Runtime的源码(objc-references.mm文件),我们得到关联对象的定义如下:(伪代码)
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
class ObjcAssociation {
uintptr_t _policy;
id _value;
};
|
可见关联对象的本质就是一个C++的ObjcAssociation对象,它内部存储着我们想要存储的数据和存储数据的策略,即objc_setAssociatedObject(...)函数的第三个、第四个参数。
然后关联对象会跟objc_setAssociatedObject(...)函数的第二个参数映射到一个叫AssociationsMap的小字典里,这个小字典维护着某个对象所有的关联对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
AssociationsMap = @{
key: ObjcAssociation,
key: ObjcAssociation,
...
}
AssociationsMap = @{
"name": name属性对应的关联对象,
"age": age属性对应的关联对象,
...
}
|
然后AssociationsMap的小字典又会跟objc_setAssociatedObject(...)函数的第一个参数映射到一个叫AssociationsHashMap的大字典里,这个大字典是Runtime维护的一个全局的字典,它维护着整个项目中所有对象的所有关联对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
AssociationsHashMap = @{
objcet: AssociationsMap,
objcet: AssociationsMap,
...
}
AssociationsHashMap = @{
person1: person1的AssociationsMap,
person2: person2的AssociationsMap,
...
}
|
二、获取一个类所有的成员变量。实现一键归档解裆
我们知道把一个复杂对象存储进NSUserDefaults的时候,必须先把复杂对象归档为NSData再存进去,读取的时候也必须先把NSData读出来然后再解裆为复杂对象。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| -----------NSUserDefaults+INESaveComplexObject.h-----------
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface NSUserDefaults (INESaveComplexObject)
- (void)ine_setComplexObject:(id)value forKey:(NSString *)defaultName;
- (id)ine_complexObjectForKey:(NSString *)defaultName;
@end
-----------NSUserDefaults+INESaveComplexObject.m-----------
#import "NSUserDefaults+INESaveComplexObject.h"
@implementation NSUserDefaults (INESaveComplexObject)
- (void)ine_setComplexObject:(id)value forKey:(NSString *)defaultName {
NSData *writeData = [NSKeyedArchiver archivedDataWithRootObject:value];
[[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] setObject:writeData forKey:defaultName];
}
- (id)ine_complexObjectForKey:(NSString *)defaultName {
NSData *readData = [[NSUserDefaults standardUserDefaults] objectForKey:defaultName];
return [NSKeyedUnarchiver unarchiveObjectWithData:readData];
}
@end
|
而对象在归档解裆时又必须遵循NSCoding协议,并实现协议里的encodeWithCoder:、initWithCoder:方法,我们总不能把项目里所有的对象的所有的成员变量都这么写一遍吧,那样工作量太大了,并且这种重复的工作似乎没太大意义,于是可以考虑使用Runtime来做。给NSObject添加一个分类,让它遵循NSCoding协议,并且实现协议里的encodeWithCoder:、initWithCoder:方法,我们调用Runtime得API遍历一个类所有的成员变量,实现一键归解档。
三、使用Method Swizzling
使用Method Swizzling需要注意以下几点:
方法交互操作一定要写在+load方法里,而不能写在+initialize方法里。因为+load方法是在类和分类加载到内存的时候调用的,不管代码里使用或者不使用这个类的分类都会被调用,而+initialize则是类被初始化的时候调用的,项目里没有用到这个类就不会被调用,所以要写在+load方法确保方法交换成功。
方法交换操作一定要写在dispatch_once里。算然说+load方法本身只会执行一次,但是并不能确保其他人不会再某些地方主动再调用一次+load方法,这就可能导致又把两个方法的实现给交换回去了。
在我们自己写的方法里,要判断一下触发了该方法的类是不是当前类,以免把类簇里的子类方法也替换掉。(例如下面的UIButton和UITableView就有类簇,OC中大量使用了类簇,我们常用的NSString、NSArray、NSDictionary等都采用类簇的形式实现)
在我们自己写的方法里,记得要调用一些方法的原生实现(除非你非常确定不需要调用方法的原生实现),因为不调用一下的话,就可能因为丢掉方法的原生实现而导致不可预知的bug。
我们知道所有继承自UIControl的类,在处理事件时都会首先调用sendAction:to:forEvent:方法,我们可以交换它的实现来防止Button的暴力点击。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
| #import "UIButton+INEPreventViolentClick.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
#define kTimeInterval 0.5
@interface UIButton ()
@property (nonatomic, assign) NSTimeInterval ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp;
@end
@implementation UIButton (INEPreventViolentClick)
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
SEL originalSelector = @selector(sendAction:to:forEvent:);
SEL swizzledSelector = @selector(ine_sendAction:to:forEvent:);
Method originalMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, originalSelector);
Method swizzledMethod = class_getInstanceMethod(self, swizzledSelector);
IMP originalIMP = method_getImplementation(originalMethod);
IMP swizzleIMP = method_getImplementation(swizzledMethod);
const char *originalTypeEncoding = method_getTypeEncoding(originalMethod);
const char *swizzledTypeEncoding = method_getTypeEncoding(swizzledMethod);
BOOL didAddMethod = class_addMethod(self, originalSelector, swizzleIMP, swizzledTypeEncoding);
if (didAddMethod) {
class_replaceMethod(self, swizzledSelector, originalIMP, originalTypeEncoding);
} else {
method_exchangeImplementations(originalMethod, swizzledMethod);
}
});
}
- (void)ine_sendAction:(SEL)action to:(nullable id)target forEvent:(nullable UIEvent *)event {
if ([[self class] isEqual:[UIButton class]]) {
NSTimeInterval currentTimeClickTimestamp = [[NSDate date] timeIntervalSince1970];
if (currentTimeClickTimestamp - self.ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp < kTwoTimeClickTimeInterval) {
return;
} else {
self.ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp = currentTimeClickTimestamp;
[self ine_sendAction:action to:target forEvent:event];
}
} else {
[self ine_sendAction:action to:target forEvent:event];
}
}
- (void)setine_lastTimeClickTimestamp:(NSTimeInterval)ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp", @(ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSTimeInterval)ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp {
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_lastTimeClickTimestamp") doubleValue];
}
@end
|
2、刷新TableView、CollectionView时,自动判断是否该显示暂无数据

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
|
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
@interface UITableView (INEPromptImage)
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ine_promptImageName;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *ine_promptText;
@property (nonatomic, copy) void(^ine_didTapPromptImage)(void);
@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL ine_dontUseThisCategory;
@end
#import "UITableView+INEPromptImage.h"
#import <objc/runtime.h>
@interface UITableView ()
@property (nonatomic, assign) BOOL ine_hasInvokedReloadData;
@property (nonatomic, strong) UIButton *ine_promptImageView;
@end
@implementation UITableView (INEPromptImage)
+ (void)load {
static dispatch_once_t onceToken;
dispatch_once(&onceToken, ^{
[self methodSwizzlingWithOriginalSelector:@selector(reloadData) swizzledSelector:@selector(ine_reloadData)];
});
}
- (void)ine_reloadData {
if ([[self class] isEqual:[UITableView class]] && !self.ine_dontUseThisCategory) {
[self ine_reloadData];
if (self.ine_hasInvokedReloadData) {
[self ine_handlePromptImage];
} else {
self.ine_hasInvokedReloadData = YES;
}
} else {
[self ine_reloadData];
}
}
#pragma mark - private method
- (void)ine_handlePromptImage {
if ([self ine_dataIsEmpty]) {
[self ine_showPromptImage];
}else {
[self ine_hidePromptImage];
}
}
- (BOOL)ine_dataIsEmpty {
NSInteger sections = 0;
if ([self.dataSource respondsToSelector:@selector(numberOfSectionsInTableView:)]) {
sections = [self numberOfSections];
} else {
sections = 1;
}
if (sections == 0) {
return YES;
}
for (int i = 0; i < sections; i ++) {
NSInteger rows = [self numberOfRowsInSection:i];
if (rows != 0) {
return NO;
}
}
return YES;
}
- (void)ine_showPromptImage {
if (self.ine_promptImageView == nil) {
self.ine_promptImageView = [[UIButton alloc] initWithFrame:CGRectMake(0, 0, 60, 90)];
self.ine_promptImageView.backgroundColor = [UIColor clearColor];
self.ine_promptImageView.contentMode = UIViewContentModeCenter;
self.ine_promptImageView.userInteractionEnabled = YES;
self.ine_promptImageView.adjustsImageWhenHighlighted = NO;
[self.ine_promptImageView setTitleColor:Color_With_RGB(170, 170, 170, 1) forState:(UIControlStateNormal)];
self.ine_promptImageView.titleLabel.font = [UIFont systemFontOfSize:12];
if (String_Is_Empty(self.ine_promptText)) {
self.ine_promptText = @"暂无数据";
}
[self.ine_promptImageView setTitle:self.ine_promptText forState:(UIControlStateNormal)];
if (self.ine_promptImageName.length == 0) {
self.ine_promptImageName = @"BaseProject_NoDataPromptImage";
}
[self.ine_promptImageView setImage:[UIImage imageNamed:self.ine_promptImageName] forState:(UIControlStateNormal)];
[self.ine_promptImageView layoutImageAndTitle:(ImageAndTitleLayoutStyleImageOnLabel) imageTitleSpace:5];
UITapGestureRecognizer *tapGestureRecognizer = [[UITapGestureRecognizer alloc] initWithTarget:self action:@selector(ine_didTapPromptImage:)];
[self.ine_promptImageView addGestureRecognizer:tapGestureRecognizer];
}
self.backgroundView = self.ine_promptImageView;
}
- (void)ine_hidePromptImage {
self.backgroundView = nil;
}
- (void)ine_didTapPromptImage:(UITapGestureRecognizer *)tapGestureRecognizer {
if (self.ine_didTapPromptImage) {
self.ine_didTapPromptImage();
}
}
#pragma mark - setter, getter
- (void)setine_hasInvokedReloadData:(BOOL)ine_hasInvokedReloadData {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_hasInvokedReloadData", @(ine_hasInvokedReloadData), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (BOOL)ine_hasInvokedReloadData {
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_hasInvokedReloadData") boolValue];
}
- (void)setine_promptImageView:(UIImageView *)ine_promptImageView {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_promptImageView", ine_promptImageView, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (UIImageView *)ine_promptImageView {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_promptImageView");
}
- (void)setine_promptText:(NSString *)ine_promptText {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_promptText", ine_promptText, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)ine_promptText {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_promptText");
}
- (void)setine_promptImageName:(NSString *)ine_promptImageName {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_promptImageName", ine_promptImageName, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)ine_promptImageName {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_promptImageName");
}
- (void)setine_didTapPromptImage:(void (^)(void))ine_didTapPromptImage {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_didTapPromptImage", ine_didTapPromptImage, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY);
}
- (void (^)(void))ine_didTapPromptImage {
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_didTapPromptImage");
}
- (void)setine_dontUseThisCategory:(BOOL)ine_dontUseThisCategory {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_dontUseThisCategory", @(ine_dontUseThisCategory), OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
- (BOOL)ine_dontUseThisCategory {
return [objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @"ine_dontUseThisCategory") boolValue];
}
@end
|






